In Text Question Answer-Chapter 10-The Constitution of India — An Introduction-Subject Social Science Class 7
Important InText Questions:
1. What is a constitution, and why do we need one?
Answer:
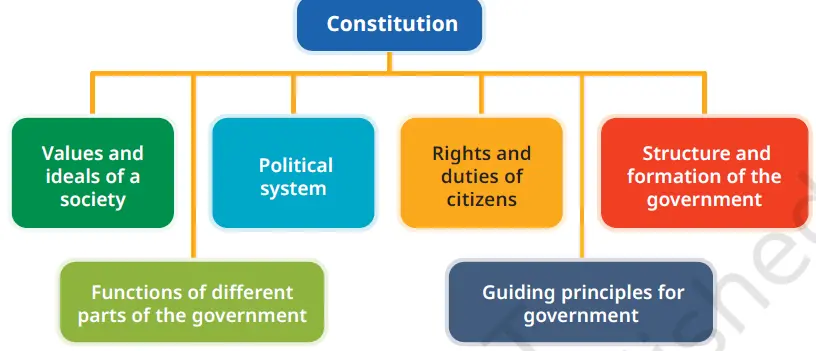
A constitution is a written document that outlines the fundamental principles, laws, and framework for governance in a country.
It defines the roles and powers of the legislature, executive, and judiciary.
It ensures the rights and duties of citizens, promoting justice, liberty, and equality.
Like a rulebook, it maintains order, accountability, and fairness in governance.
Without a constitution, there would be confusion, misuse of power, and no legal protection for people.
2. How was the Indian Constitution prepared?
Answer:
The Constituent Assembly was formed in 1946 to draft the Constitution.
It initially had 389 members (later 299 after Partition) representing India’s diversity.
Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the Chairman, and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar chaired the Drafting Committee.
The Assembly held intense debates and discussions over nearly 3 years (1946–1949).
The final draft was adopted on 26 November 1949 and came into effect on 26 January 1950.
More:
3. How did our freedom struggle and civilisational heritage influence the Constitution?
The freedom movement contributed values like equality, liberty, justice, and fraternity.
Civilisational heritage added ideals like Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam, respect for diversity, and duty towards nature.
The Constitution also reflects ancient traditions of participatory governance and moral responsibility.
4. What are the key features of the Constitution of India? Why is it still relevant today?
Key Features:
Separation of powers: legislature, executive, judiciary.
Fundamental Rights and Duties.
Directive Principles of State Policy.
Federal structure (Central, State, Local governments).
Relevance:
Continues to protect citizens’ rights.
Evolved through amendments.
Guides governance in a diverse, democratic country.
5. Can you find out the amendments made to the Constitution in the past ten years?
Yes, some important amendments from the last 10 years include:
101st Amendment (2016): Introduced Goods and Services Tax (GST).
103rd Amendment (2019): 10% reservation for EWS (Economically Weaker Sections).
104th Amendment (2020): Removed reserved seats for Anglo-Indians in Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
105th Amendment (2021): Gave states power to identify backward classes.
Additional Questions:
2 Marks Questions (Short Answers)
What is meant by ‘Fraternity’ in the Constitution?
→ Fraternity means a sense of brotherhood among all citizens, ensuring no one is treated as inferior.Who wrote the Constitution by hand and illustrated it?
→ Calligrapher Prem Behari Narain Raizada wrote it by hand; illustrations were done by Nandalal Bose and his team.What is the significance of the Preamble?
→ It summarises the core values and principles of the Constitution like Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity.What are Fundamental Duties? Give two examples.
→ Fundamental Duties are moral obligations of citizens added by the 42nd Amendment.
Examples:To respect the Constitution and national symbols.
To protect the environment.
5. How is the Indian Constitution a ‘living document’?
→ It evolves through amendments, reflects current needs, and remains relevant.
Example: Right to Education and inclusion of Panchayati Raj.6. What values did the Indian freedom movement contribute to the Constitution?
→ Equality, non-discrimination, justice, unity, and respect for all religions and communities.
5 Marks Questions (Detailed Answers)
Explain the structure and organs of the government defined in the Constitution.
→ The Constitution defines three main organs:Legislature: Makes laws (Parliament).
Executive: Implements laws (President, PM, Council of Ministers).
Judiciary: Interprets laws and ensures justice (Supreme Court, High Courts).
It also defines a three-tier government system: Central, State, and Local (Panchayats).
How is the Constitution influenced by other countries? Give examples.
→ Indian Constitution borrowed features from many democracies:France: Liberty, Equality, Fraternity.
USA: Fundamental Rights and independent judiciary.
UK: Parliamentary system.
Ireland: Directive Principles.
These were adapted to suit Indian conditions.
To Learn More In Text Questions Click Below:
Chapter 3- Climates of India
Chapter 4- New Beginnings: Cities and States
Chapter 5-The Rise of Empires
Chapter 6- The Age of Reorganisation
Chapter 7- The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
Chapter 8- How the Land Becomes Sacred
Chapter 9 –From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
**************************************
MCQs:
Chapter 1- Geographical Diversity of India
Chapter 2- Understanding the Weather
Chapter 3- Climates of India
Chapter 4- New Beginnings: Cities and States
Chapter 5- The Rise of Empires
Chapter 6- The Age of Reorganisation
Chapter 7 – The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
Chapter 8- How the Land Becomes Sacred
Chapter 9 –From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
**************************************
NCERT Solutions:
Chapter 1- Geographical Diversity of India
Chapter 2- Understanding the Weather
Chapter 3- Climates of India
Chapter 4- New Beginnings: Cities and States
Chapter 5–The Rise of Empires
Chapter 6- The Age of Reorganisation
Chapter 7 – The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
Chapter 8- How the Land Becomes Sacred
Chapter 9 –From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
I want the lesson 10 , 11,and 12
Please send that also